Difference between revisions of "Merging CAGE experiments"
Ivan@dote.ru (talk | contribs) (→Algorithm overview) |
Ivan@dote.ru (talk | contribs) (→Algorithm overview) |
||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
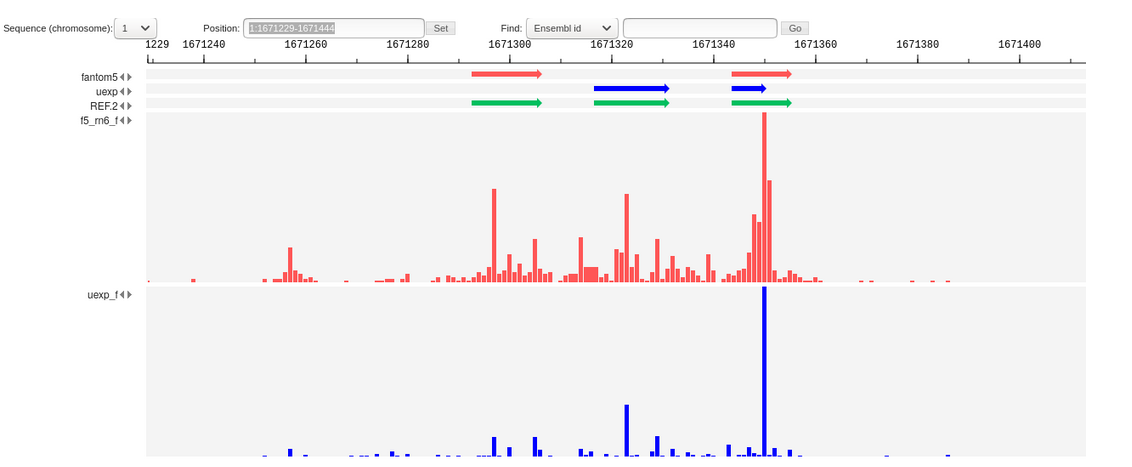
[[File:CAGE_merging_merge_reference_peaks.png|frame|center|Figure 4. One new peak to several reference peaks.]] | [[File:CAGE_merging_merge_reference_peaks.png|frame|center|Figure 4. One new peak to several reference peaks.]] | ||
| + | |||
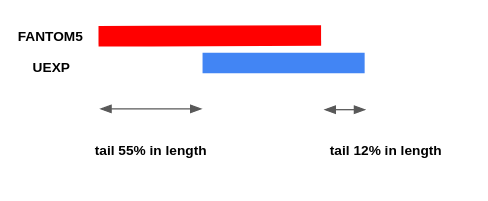
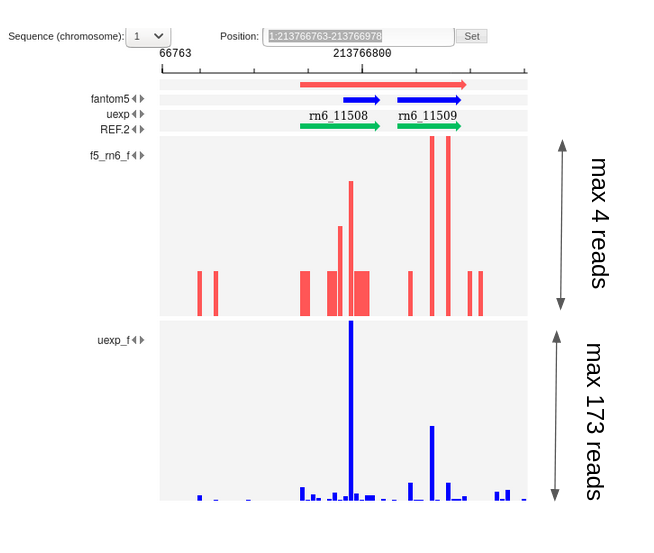
| + | A preliminary analysis of the rat CAGE data (Reference = FANTOM5, NewData = UEXP) showed a significant length of the overhangs (the average overhang length is 55% of the peak length for FANTOM5 peaks and 12% for UEXP peaks) as well as a significant proportion of multiple intersections (7.5% FANTOM5 peaks intersect with more than one UEXP peak and 1.1% of UEXP peaks intersect with more than one FANTOM5 peak). | ||
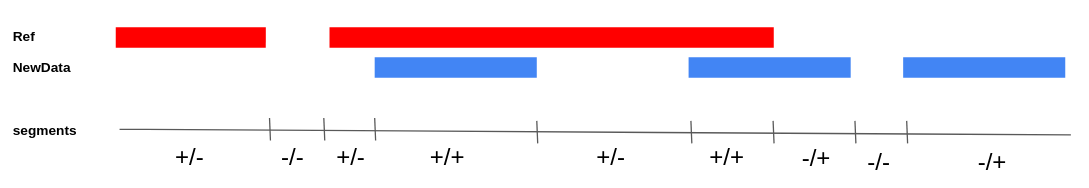
[[File: Algorithm_segments.png|Segmentation of CAGE peaks]] | [[File: Algorithm_segments.png|Segmentation of CAGE peaks]] | ||
Revision as of 16:01, 4 March 2021
Merging CAGE experiments. This page describes the problem of merging independent CAGE-seq experiments and approaches to solving it.
Problem statement
Transcription of genes begins at genomic positions called transcription start sites (TSS). CAGE is a high-throughput transcriptome analysis technique that can identify active TSSs with one base resolution and their relative activities. It was shown by CAGE method that different sets of TSSs can operate under different conditions, and that transcription can start from several closely spaced TSSs within the promoter. All this complicates the comparative analysis of CAGE experiments carried out in different conditions. We have developed a method that allow us to combine independent CAGE experiments and to obtain a pooled set of TSSs with accurately defined boundaries. Iterative application of this method to a large set of CAGE experiments allows the construction of a reference TSS set. The presence of such a reference set makes it easy to compare TSS activities in different experiments, as well as to identify previously unknown TSS in the incoming data.
Algorithm overview
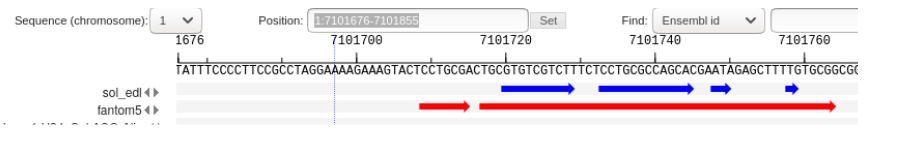
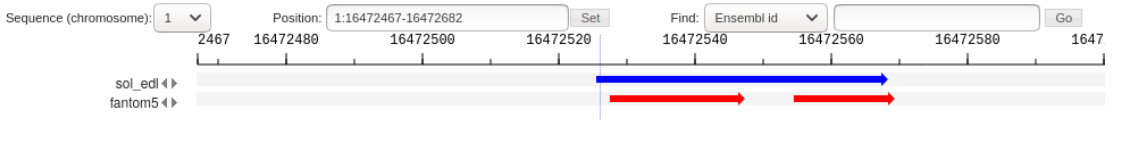
The method accepts two data sets (Reference and NewData) as input. Each of the sets consists of CAGE peaks and a corresponding full genome profile of the 5' ends of CAGE reads. The result is a set of non-overlapping NewReference peaks that reflect all TSSs from the input sets. If we intersect two sets of CAGE peaks (Reference and NewData) at genomic coordinates, the following types of peaks can be identified (Fig. 1):
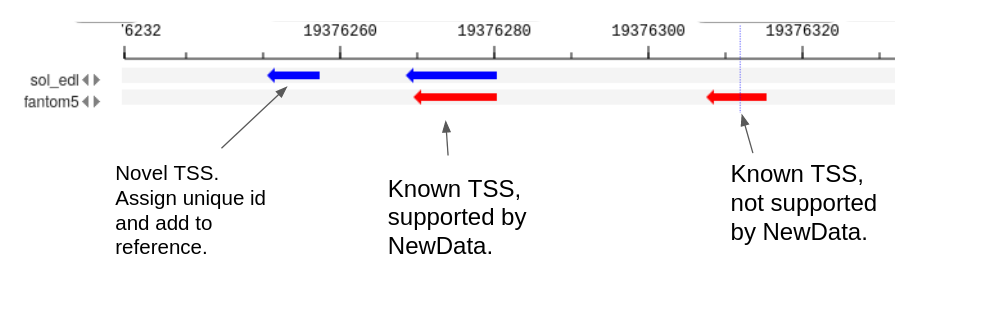
- Previously unknown - NewData peaks do not intersect with Reference peaks.
- Not active in NewData - Reference peaks do not intersect with NewData.
- Previously known, active in NewData - intersecting peaks Reference and NewData.
The first two types of peaks go into the NewReference set without changes, and for the third, it is necessary to clarify the boundaries, since the intersection can be partial. when there is a partial intersection of the Reference and NewData peaks, overhanging ends (Fig. 2) as well as multiple intersections (Fig. 3, Fig. 4) can be observed.
A preliminary analysis of the rat CAGE data (Reference = FANTOM5, NewData = UEXP) showed a significant length of the overhangs (the average overhang length is 55% of the peak length for FANTOM5 peaks and 12% for UEXP peaks) as well as a significant proportion of multiple intersections (7.5% FANTOM5 peaks intersect with more than one UEXP peak and 1.1% of UEXP peaks intersect with more than one FANTOM5 peak).